3 Years Later, Genocide of Yazidis by ISIS Still Ongoing

Iraq's Yazidis marked three years since Islamic State launched what the United Nations said was a genocidal campaign against them on Thursday, but their ordeal is far from over despite the ouster of the jihadist fighters.
Militants were driven out of the last part of the Yazidi homeland in northern Iraq in May. However, most Yazidis have yet to return to villages they fled when Islamic State over-ran Sinjar in the summer of 2014, killing and capturing thousands because of their faith.
Nearly 3,000 Yazidi women and children remain in Islamic State captivity, and control over Sinjar is disputed by rival armed factions and their regional patrons. Justice for the crimes Yazidis suffered, including sexual enslavement, has also so far proved elusive.
"The Yazidis' wound is still bleeding," one man told Reuters at a ceremony attended by several thousand people including the mayor and other local dignitaries, held at a temple at the foot of the mountain that dominates Sinjar.
"The Kurds and the Iraqi government are fighting for Sinjar and we are paying the price," said the man.
A U.N. human rights Commission of Inquiry, which declared the killings of thousands of Yazidis to be a genocide, said on Thursday that the atrocity had not ended and that the international community was not doing enough to stop it.
"The genocide is ongoing and remains largely unaddressed, despite the obligation of States ... to prevent and to punish the crime," the commissioners said in a statement.
Islamic State fighters killed thousands of captured men during their attack on the Yazidis, a religious sect whose beliefs combine elements of several ancient Middle Eastern religions. Islamic State considers Yazidis as devil-worshippers.
Images of desperate Yazidis fleeing up the mountain in the blazing summer heat were broadcast around the world and helped to galvanize the United States to conduct its first air strikes against Islamic State in Iraq.
At least 9,900 of Iraq's Yazidis were killed or kidnapped in just days in the Islamic State attack in 2014, according to a study documenting the number of Yazidis affected which could be used as evidence in any trial for genocide.
About 3,100 Yazidis were killed — with more than half shot, beheaded or burned alive — and about 6,800 kidnapped to become sex slaves or fighters, according to the report published in the Public Library of Science journal PLoS Medicine.
Enslaved women and girls are now reportedly being sold by Islamic State fighters trying to escape the U.S.-led assault on their Syrian stronghold of Raqqa, the U.N. commission said.
DISPUTE OVER SINJAR
The array of forces that drove Islamic State out of Sinjar are now vying for control of the area near the borders of Iraq, Syria and Turkey.
Kurdish peshmerga forces retook around half of Sinjar in late 2015, effectively annexing it to the autonomous region they hope to convert into an independent state. A referendum on independence is due to be held in September, which the government in Baghdad opposes.
Mainly Shi'ite paramilitary groups, some backed by Iran, retook the rest of the Yazidi homeland in May, bringing them within meters of the peshmerga.
Another group, the outlawed Kurdistan Workers Party (PKK), also gained a foothold in Sinjar and clashed with the peshmerga earlier this year. Its presence has made the area a target for Turkey, which has fought a three-decade war against the PKK on its own soil.
"People are worried about returning," said General Ashti Kojer, the local head of Kurdish police, known as Asayish. "The (Sinjar) region has become a conflict zone".
Kojer and another local official said the political environment was preventing international organizations from working on reconstruction and rehabilitation in Sinjar, further discouraging Yazidis from returning.
Water has to be trucked in, electricity is supplied from private generators, schools are closed, and the closest hospital is Dohuk -- around three hours' drive away.
"The lack of services and political problems are preventing families from returning," Jalal Khalaf, the director of the mayor's office in Sinjar, told Reuters.
BLAME GAME
In a speech at the ceremony, the Yazidi mayor of Sinjar, Mahma Xelil, said former Iraqi Prime Minister Nuri al-Maliki was responsible for the tragedy because he was in charge when the militants overran Mosul, capturing billions of dollars of weapons they used in their attack on the minority.
Other Yazidis blame the Kurds, who were defending the area at the time, for failing to resist the IS onslaught.
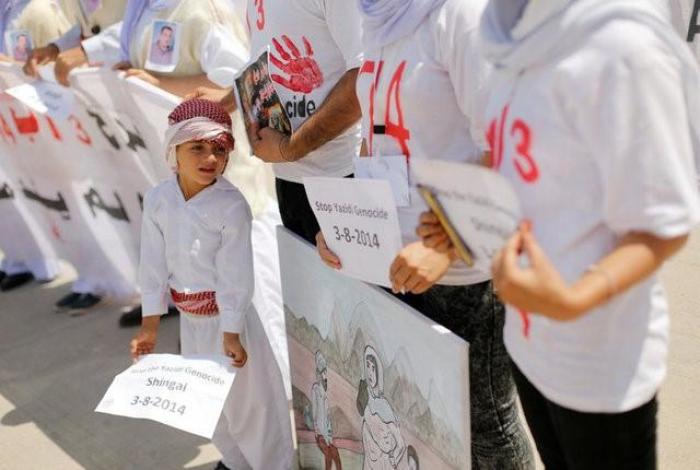
At the ceremony, people carried signs saying "Stop Yazidi Genocide." Families streamed into cemeteries to remember their loved ones. Women wore bandanas saying "Genocide."
In the city of Sinjar, posters and banners hung up on roundabouts depict harrowing scenes from the attack three years ago: families fleeing and distressed women and children.
Large parts of the city, which was also home to Muslim Kurds and Arabs, remain empty. Around 1,000 Yazidi families have returned to Sinjar since the city was retaken in 2015, according to Khalaf. The city and the surrounding area had been home to around 400,000 Yazidis.
Farhan Lazgin brought his family back to Sinjar around one year ago because he was fed up with living in a camp.
His home was in relatively good shape, but his two children have missed out on a year of school, and may fall further behind because teachers are not returning to the city.
Zeido Shammo, one of the few shopowners to have returned to the city, said he no longer trusted local forces: "We ask for international protection," he said, echoing the sentiment of many Yazidis.
Although Islamic State has been routed from the area, Shammo said he could not feel safe until their hardline ideology was eradicated too: "Daesh (Islamic State) is defeated but we are still worried because the mentality of Daesh still exists."
Opposite his shop, Islamic State slogans have yet to be painted over. One reads: "The State of the Caliphate Remains."